Tutorial 9: Regular Expressions
Main Objectives of this Practice Tutorial
- Define the term Regular Expressions
- Explain the difference between Regular Expressions and Filename Expansion
- Explain the purpose of Literal (Simple) Regular Expressions
- Understand and use common symbols for Complex Regular Expressions and their purpose
- Understand and use command symbols for Extended Regular Expressions and their purpose
- List several Linux commands that can use regular expressions
Tutorial Reference Material
Course Slides:
Regular Expressions:
Linux Commands:
| egrep | man | more / less | vi / vim | sed | awk | wget |
|---|
Instructional Videos:
Key Concepts
Regular Expressions
A regular expression is a combination of two types of characters: literals and special characters. Strings of text can be compared to this pattern to see if there is a match.
This usually refers to text that is contained inside a file or text as a result of issuing Linux commands using a Linux pipeline command.
Literal (Simple) Regular Expressions
The simplest regular expression is a series of letters and numbers, (tabs or spaces). A simple (literal) regular expression consists of normal characters, which used to match patterns.
Although there are many Linux commands that use regular expressions, the grep command is a useful command to learn how to display matches of patterns of strings within text files.
For example:
grep Linux document.txt

A simple (literal) regular expression is a series of letters and numbers (tabs or spaces).
Complex Regular Expressions
The problem with just using simple (literal) regular expressions is that only simple or general patterns are matched.
Complex Regular Expressions use symbols to help match text for more precise (complex) patterns. The most common complex regular expression symbols are displayed below:
Anchors: ^ , $
Match lines the begin (^) or end ($) with a pattern.
Single Character: .
Represents a single character that can be any type of character.
Character Class: [ ] , [^ ]
Represents a single character but with restrictions.
Zero or More Occurrence: *
Zero or more occurrences of previous character.
Examples of complex regular expressions are displayed below:

Example of using anchors. ^

Example of matching by character(s). ^
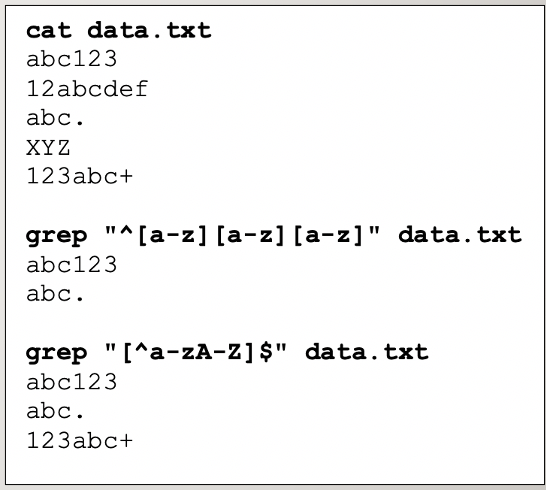
Example of using character class. ^

Example of matching zero or more occurrence of preceding character. ^
Extended Regular Expressions
Extended Regular Expressions consist of additional special characters to “extend” the capability of regular expressions. You must use the egrep or grep -E commands in order to properly use extended regular expressions.
Repetition: {min,max}
Allows for more precise repetitions. Using braces, you can specify the minimum and/or maximum number of repetitions.
Groups: ( ) Allows you to search for repetition for a group of characters, a word, or a phase. You enclose them within brackets ( ) to specify a group.
or Condition: | Can be used with groups to match a variety of character(s), words or phases. The | symbol is used to separate the variety of character(s) within a group.
Examples of how to use extended regular expressions with the egrep command are displayed below:
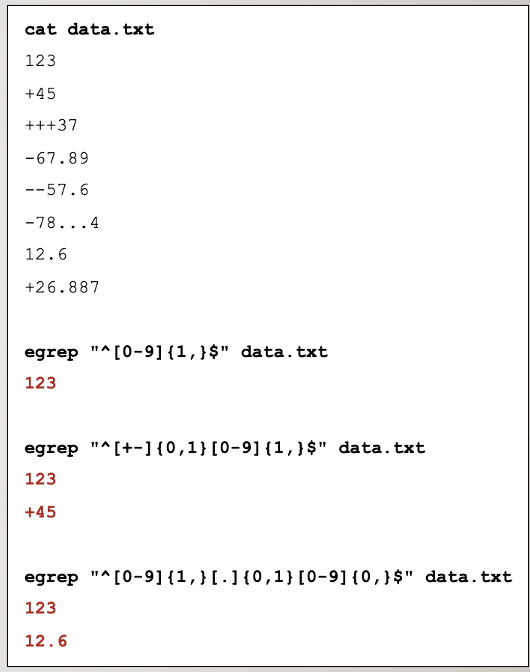
Example of using repetition. ^

Example of using groups. ^

Example of using or condition with groups. ^
Investigation 1: Simple & Complex Regular Expressions
ATTENTION: This online tutorial will be required to be completed by Friday in week 10 by midnight to obtain a grade of 2% towards this course
In this investigation, you will learn how to use the grep command with simple and complex regular expressions to help search for patterns contained in text files.
Perform the Following Steps:
- Login to your matrix account.
- Issue a Linux command to confirm you are located in your home directory.
- Issue the following linux Linux command to copy a text file to your home directory from the ULI101 home directory:
cp ~uli101/tutorialfiles/textfile1.txt ~/
View the contents of the textfile1.txt file using the more command see what data is contained in this file.
- Although there are several Linux commands that use regular expressions, we will be using the grep command for this investigation.
Issue the following Linux command to match the pattern the within textfile1.txt:
grep "the" textfile1.txt
- Take a few moments to view the output below and observe the matched patterns.

- Issue the grep Linux command with the -i option to ignore case sensitively:
grep -i "the" textfile1.txt
- What do you notice is different when issuing this command?
- You will notice that the pattern "the" is matched including larger words like "them" and "their".
- You can issue the grep command with the -w option to only match the pattern as a word.
- Issue the following Linux command:
grep -w -i "the" textfile1.txt
You should now see only strings of text that match the word the (upper or lower case).
Matching literal or simple regular expressions can be useful, but are limited in what pattens they can match. For example, you may want to search for a pattern located at the beginning or end of the string.
There are other regular expression symbols that provide more precise search pattern matching.
These special characters are known as complex and extended regular expressions symbols.
For the remainder of this investigation, we will focus on complex regular expressions and then focus on extended regular expressions in INVESTIGATION 2.
- Issue the following Linux command:
grep -w -i "^the" textfile1.txt
- The ^ symbol is referred to as an anchor.
- In this case, it only matches the word "the" (both upper or lowercase) at the beginning of the string.

- Issue the following Linux command:
grep -w -i "the$" textfile1.txt
- The $ symbol is used to anchor patterns at the end of the string.

- Issue the following Linux command to anchor the word "the" simultaneously at the beginning and end of the string:
grep -w -i "^the$" textfile1.txt
- What do you notice?
- Anchoring patterns at both the beginning and ending of strings can greatly assist for more precise search pattern matching.
- We will now be demonstrate the effectiveness of combining anchors with other complex regular expressions symbols.
- Issue the following Linux command to match strings that begin with 3 characters:
grep "^..." textfile1.txt
- What do you notice? Can lines that contain less than 3 characters be displayed?

- Issue the following Linux command to match strings that begin and end with 3 characters:
grep "^...$" textfile1.txt
- What do you notice compared to the previous command?

- Issue the following Linux command to match strings that begin with 3 digits:
grep "^[0-9][0-9][0-9]" textfile1.txt
- What did you notice?
- Issue the following Linux command to match strings that end with 3 uppercase letters:
grep "[A-Z][A-Z][A-Z]$" textfile1.txt
- What type of strings match this pattern?
- Issue the following Linux command to match strings that consist of only 3 digits:
grep "^[0-9][0-9][0-9]$" textfile1.txt
- What did you notice?
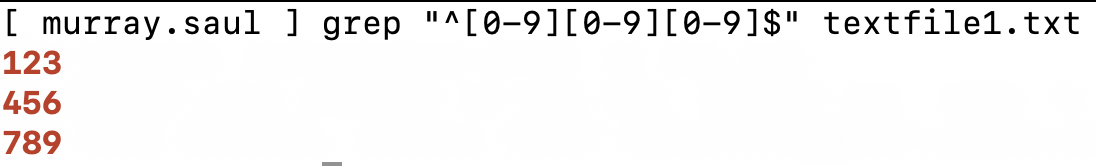
- Issue the following Linux command to match strings that consist of only 3 alphanumeric digits:
grep "^[a-zA-Z0-9][a-zA-Z0-9][a-zA-Z0-9]$" textfile1.txt
- What did you notice?

- The "*" complex regular expression symbol is often confused with the "*" filename expansion symbol.
- In other words, it does NOT represent zero or more of any character, but zero or more occurrences of the character that comes before the "*" symbol.
- To demonstrate, issue the following Linux command to display zero or more occurrences of the letter "x":
grep "x*" textfile1.txt
- You will most likely notice most lines of the file is displayed.
- Let's issue a Linux command to display strings that contain more than one occurrence of the letter "x":
grep "xx*" textfile1.txt
- Why did this work? because the pattern indicates one occurrence of the letter "x", followed by zero or MORE occurrences of the next letter "x".
- If you combine the complex regular expression symbols ".*" it will act like zero or more occurrences of any character (i.e. like "*" did in filename expansion).
- Issue the following Linux command to match strings begin and end with a number with nothing or anything inbetween:
grep "^[0-9].*[0-9]$" textfile1.txt
- Using simultaneous anchors combined with the ".*" symbol(s) can help you to refine your search patterns of strings.
- Issue the following Linux command to display strings that begin with a capital letter, end with a number, and contains a capital X somewhere inbetween:
grep "^[A-Z].*X.*[0-9]$" textfile1.txt
- Let's look at another series of examples involving searching for strings that only contain valid numbers.
- We will use pipeline commands to both display stdout to the screen and save to files for confirmation of running these pipeline commands when run a checking-script later in this investigation.
- Issue the following Linux command to create the regexps directory:
mkdir ~/regexps
- Change to the regexps directory and confirm that you have moved to this directory.
- First, issue the following Linux command to copy another data file called numbers1.dat:
cp ~uli101/tutorialfiles/numbers1.dat ~/regexps
- View the contents of the numbers.dat file using the more command and quickly view the contents of this file. You should notice valid and invalid numbers contained in this file. When finished, exit the more command.
- Issue the following linux pipeline command to display only whole numbers (i.e. no + or - sign):
grep "^[0-9]*$" numbers1.dat | tee faulty.txt
- You may have noticed that the command does not entirely work. You may notice an empty line (which is NOT a whole number). This occurs since the * regular expression symbol represents ZERO or MORE occurrences of a number. You can use an additional numeric character class with the * regular expression symbol to search for one or more occurrences of a number.
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command to display only whole numbers:
grep "^[0-9][0-9]*$" numbers1.dat | tee whole.txt
- You should see that this now works.
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command to display only signed integers:
grep "^[+-][0-9][0-9]*$" numbers1.dat | tee signed.txt
- What did you notice? Positive and negative numbers display, not unsigned numbers.
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command to display signed or unsigned integers:
grep "^[+-]*[0-9][0-9]*$" numbers1.dat | tee all.txt
- Did this command work?

- Simultaneous anchoring of regular expressions using character class and zero or more occurrences to display signed and unsigned integers.
- Issue the following command to check that you created those hard links:
~uli101/week9-check-1
If you encounter errors, then view the feedback to make corrections, and then re-run the checking script. If you receive a congratulation message that there are no errors, then proceed with this tutorial.
You can also use the grep command using regular expression as a filter in pipeline commands.
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command:
ls | grep "[0-9].*dat$"
- What did this pipeline display?
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command:
ls | grep "[a-z].*txt$"
- What did this pipeline display?
- Although very useful, complex regular expressions do NOT entirely solve our problem of displaying valid unsigned and signed numbers (not to mention displaying decimal numbers).
In the next investigation, you will learn how to use extended regular expressions that will completely solve this issue. You can proceed to INVESTIGATION 2.
Investigation 2: Extended Regular Expressions
In this investigation, you will learn how to use extended regular expressions with the egrep command to further refine your search patterns.
Perform the Following Steps:
- Make certain that you are located in your ~/regexps directory on your Matrix account.
- Issue the following Linux command to copy another data file called numbers2.dat:
cp ~uli101/tutorialfiles/numbers2.dat ~/regexps
- View the contents of the numbers2.dat file using the more command and quickly view the contents of this file. You should notice valid and invalid numbers contained in this file. When finished, exit the more command.
- Issue the following Linux command to display signed or unsigned integers:
grep "^[+-]*[0-9][0-9]*$" numbers2.dat
- You should notice multiple + or - signs appear prior to some numbers.
- This occurs since you are searching or one or MORE occurrences of a + or - sign.

- Weakness of complex regular expressions that do not limit the number of positive or negative signs.
- Using extended regular expression symbols to specify minimum and maximum repetitions: {min,max} can solve that problem.
- Issue the following Linux command (using extended regular expression symbols) to display signed or unsigned integers:
grep "^[+-]{0,1}[0-9]{1,}$" numbers2.dat
- NOTE: No output will be displayed! Why?
- This is due to the fact that the grep command was NOT issued correctly to use extended regular expression symbols.
- You would need to issue either grep -E, or just issue the egrep command. The egrep command works with all regular expression symbols, and should be used in the future instead of the older grep command.
- We will use pipeline commands to both display stdout to the screen and save to files for confirmation of running these pipeline commands when run a checking-script later in this investigation.
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command using egrep instead of grep:
egrep "^[+-]{0,1}[0-9]{1,}$" numbers2.dat | tee better-number1.txt
- You should have noticed that the command worked correctly this time because you used the egrep command.

- Using extended regular expression symbols (such as repetition) to refine matches of signed and unsigned integers.
- NOTE: With extended regular expressions, the ? symbol can be used to represent the {0,1} repetition symbols and the + symbol can be used to represent the {1,} repetition symbols
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command using the repetition shortcuts "+" and "?":
egrep "^[+-]?[0-9]+$" numbers2.dat | tee better-number2.txt
- You should have seen the same results, but less typing was required.
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command to display signed, unsigned, whole, and decimal numbers:
egrep "^[+-]{0,1}[0-9]{1,}[.]{0,1}[0-9]*$" numbers2.dat | tee better-number3.txt
- Were all signed and unsigned intergers and decimal numbers displayed?
- Issue the follwoing command to check that you correctly issued those Linux pipeline commands:
~uli101/week9-check-2
- If you encounter errors, then view the feedback to make corrections, and then re-run the checking script.
- If you receive a congratulation message that there are no errors, then proceed with this tutorial.
- You can also use extended regular expression symbols for grouping. For example, you can search for repetitions of GROUPS of characters (like a word) as opposed to just a single character or a GROUP of numbers as opposed to a single digit.
- Issue the following linux pipeline command to copy another data file called words.dat:
cp ~uli101/tutorialfiles/words.dat ~/
View the contents of the words.dat file using the more command and quickly view the contents of this file. Within this file, you should notice some lines that contain repetitions of words. When finished, exit the more command.
Issue the following linux pipeline command to display two or more occurrences of the word "the":
egrep -i "(the){2,}" words.dat | tee word-search1.txt more
- NOTE: No output is displayed! Why?
- This is due to the fact that a space should be included at the end of the word "the". Usually words are separated by spaces; therefore, there were no matches since there were not occurrences of "thethe" as opposed to "the the" (i.e. no space after repetition of the pattern).
- Reissue the previous pipeline command with the word the followed by a space within the brackets:
egrep -i "(the ){2,}" words.dat | tee word-search2.txt
- The "|" (or) symbol (same symbol as "pipe") can be used within the grouping symbols to allow matching of additional groups of characters. Again, it is important to follow the character groupings with the space character

- Using extended regular expression symbols (such as grouping) to refine matches of repetition of words (as opposed to characters).
- Issue the following linux pipeline command to search for two or more occurrences of the word "the " or two or more occurrences of the word "and ":
egrep -i "(the |and ){2,}" words.dat | tee word-search3.txt
- Issue the following Linux command to check that you correctly issued those Linux pipeline commands using the tee command to create those text files:
~uli101/week9-check-3
- If you encounter errors, then view the feedback to make corrections, and then re-run the checking script.
- If you receive a congratulation message that there are no errors, then proceed with this tutorial.
- Let's issue a Linux pipeline command using the egrep command as a filter using both complex and extended regular expressions.
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command:
ls | egrep "[a-z]{1,}.*[0-9]"
- What did this Linux pipeline command display?
- The grep and egrep Linux commands are NOT the only Linux commands that use regular expressions.
In the next investigation, you will apply regular expressions to a number of Linux commands that you already learned in this course.
You can proceed to INVESTIGATION 3
Investigation 3: Other Commands Using Regular Expressions
In this investigation, you will see commands other than grep or egrep that can use regular expressions.
Perform the Following Steps:
- Make certain that you are located in your ~/regexps directory on your Matrix account.
- Let's look at using regular expressions with the man command. Issue the following linux command :
man ls
- We want to search for an option that can sort the file listing. Type the following regular expression below and press ENTER:
/sort

- Entering /sort in the man command can search for the string "sort".
- FYI: The grep and egrep Linux commands contain the regular expressions within quotes, but most other Linux commands specify regular expressions using forward slashes (e.g. /regular expression or /regular expression/).
Scroll throughout the man pages for the ls command to view matches for the pattern "sort" (You can press SPACE or key combination alt-b to move forward and backwards one screen respectively).
Press the letter
qto exit the man pages for ls.- Let's use regular expressions with the less command.
Issue the following Linux command to copy another data file called large-file.txt:
cp ~uli101/tutorialfiles/large-file.txt ~/
- Issue the following Linux command to view the contents of the large-file.txt:
less large-file.txt
- We want to search for a pattern uli101 within this text file. Type the following regular expression and press ENTER:
/uli101
- You should see the pattern "uli101" throughout the text file.

- Entering /uli101 in the less command can display all matches of "uli101" throughout the text file.
Press the letter
qto exit the less command.Try the same search techniques with the more command.
- Does it work the same for the less command?
- Let's learn how to perform a simple search and replace within the vi utility by using regular expressions.
Issue the following Linux command to edit the large-file.txt file:
vi large-file.txt
- Let's first perform a simple search within this text file.
- Press the ESC key to make certain you are in COMMAND mode.
- Type the following and press ENTER:
/uli101
- You should notice the pattern "uli101" highlighted for ALL occurrences in this text file.

- Entering /uli101 in the vi command can search for the string "uli101".
- Let's search for the uli101 pattern, and replace it in capitals (i.e ULI101).
- In vi, to issue a command, you need to enter LAST LINE MODE then issue a command.
- Let's issue a command from LAST LINE MODE to search and replace uli101 to ULI101.
- Making certain that you are COMMAND MODE in vi, type the following and press ENTER:
:%s/uli101/ULI101/g
- NOTE: The letter g after the replace regular expression represents "global" and will replace ALL occurrences of uli101 in the text document (as opposed to replacing the first occurrence for every line).
- Type the following (in uppercase letters) and press ENTER:
/ULI101
- You should notice the pattern "ULI101" highlighted for ALL occurrences in this text file.

- In last line MODE in the vi text editor, issuing a command using regular expressions to convert uli101 to ULI101.
- Navigate throughout the text file to confirm that ALL occurrences of uli101 have been replaced with ULI101.
- Save changes to your vi editing session and exit by typing the following and pressing ENTER:
:x
Linux Practice Questions
The purpose of this section is to obtain extra practice to help with quizzes, your midterm, and your final exam.
Review Questions: Simple & Complex Regular Expressions
Here is a link to the MS Word Document of ALL of the questions displayed below but with extra room to answer on the document to simulate a quiz: Week 9 - Command Practice 9a
Your instructor may take-up these questions during class. It is up to the student to attend classes in order to obtain the answers to the following questions. Your instructor will NOT provide these answers in any other form (eg. e-mail, etc).
Part A: Display Results from Linux Commands using Simple & Complex Regular Expressions
Note the contents from the following tab-delimited file called ~uli101/cars:
Plym fury 77 73 2500
chevy nova 79 60 3000
ford mustang 65 45 10003
volvo gl 78 102 9850
ford ltd 83 15 10507
chevy nova 80 50 3503
fiat 600 65 115 450
honda accord 81 30 6000
ford thundbd 84 10 17000
toyota tercel 82 180 755
chevy impala 65 85 1553
ford bronco 83 25 9505
Write the results of each of the following Linux commands using regular expressions for the above-mentioned file.
grep plym ~uli101/carsgrep -i fury ~uli101/carsgrep “^[m-z]” ~uli101/carsgrep -i “^[m-z]” ~uli101/carsgrep “3$” ~uli101/carsgrep -i “c.*5$” ~uli101/cars
Part B: Writing Linux Commands Using Regular Expressions
Write a single Linux command to perform the specified tasks for each of the following questions.
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/text.txt that contains the pattern: the
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/text.txt that contains the word: the
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/text.txt that begin with a number.
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/text.txt that end with a letter (either upper or lowercase).
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/text.txt that begin and end with a number.
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/text.txt that contains exactly 3 characters that can be anything.
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/text.txt that contains exactly 3 numbers.
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/text.txt that contains 1 or more “C” characters.
Review Questions: Regular Expressions (Including Extended Regular Expressions)
Here is a link to the MS Word Document of ALL of the questions displayed below but with extra room to answer on the document to simulate a quiz: Week 9 - Command Practice 9b
Your instructor may take-up these questions during class. It is up to the student to attend classes in order to obtain the answers to the following questions. Your instructor will NOT provide these answers in any other form (eg. e-mail, etc).
Part A: Display Results from Linux Commands using Regular Expressions
Note the contents from the following tab-delimited file called ~uli101/numbers.txt:
+123
---34
+++++++++++17
-45
45p8
25.6
11
Write the results of each of the following Linux commands using regular expressions for the above-mentioned file.
grep "^[-+]" ~uli101/numbers.txtgrep "^[-+]*.[0-9]" ~uli101/numbers.txtgrep "^[+-]?[0-9]" ~uli101/numbers.txt- (Why?)
egrep "^[+-]?[0-9]" ~uli101/numbers.txtegrep "^[+-]?[0-9]+$" ~uli101/numbers.txtegrep "^[+-]?[0-9]+[.]?[0-9]+$" ~uli101/numbers.txt
Part B: Writing Linux Commands Using Regular Expressions
Write a single Linux command to perform the specified tasks for each of the following questions.
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/data.txt that begins with 1 or more occurrences of an UPPERCASE letter.
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/data.txt that ends with 3 or more occurrences of the number 6
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/data.txt that begins with 2 or more occurrences of the word “the” (upper or lower case).
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/data.txt that begins with 2 or more occurrences of the word “the” or the word “but” (upper or lower case).
- Write a Linux command to display all lines in the file called ~/data.txt that begins with a minimum of 2 occurrences and a maximum of 4 occurrences of the word “the” or the word “but” (upper or lower case).
Author: Murray Saul
License: LGPL version 3 Link: https://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html